Last modified: March 08, 2023
In Class Lab A4.10 Love Chase
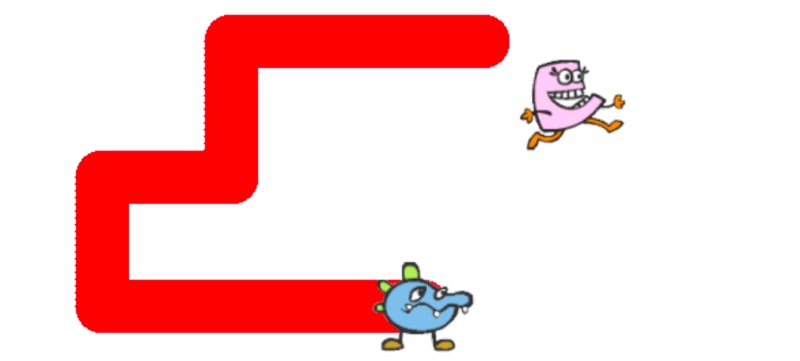
Long long ago, in a mystery land far away
lived two little mosters, Bluey Blue and Pinky Pink.
Pinky Pink is madly in love with Bluey Blue, but...
alas, Bluey Blue doesn't want anything to do with Pinky Pink...
on the surface.
The truth is, Bluey Blue is madly in love with Pinky Pink too;
its just that Bluey Blue is too shy to say it out loud.
But wherever Bluey Blue goes, he leaves behind a trace
so that Pinky Pink can catch up with him sooner or later.
Eventually, Bluey Blue stopped to wait for Pinky Pink.
The couple finally unites, and a little heart appears 💕
In this lab, you will recreate the legend of Bluey Blue and Pinky Pink.
You can download a demo of this lab here.
You may use the sprites from the demo's /images folder, or any images of your preference.
Creating Bluey Blue
According to the legend, Blue "leaves behind a trace" wherever he goes so that Pinky Pink can follow the trace.
In Java, you can represent this idea of "trace" using the Point class together with the ArrayList class:
- The Point class:
- can store a particular x and y coordinate
- offers methods to calculate the distance between two points, determine if two points overlap, etc.
- The ArrayList class:
- stores a collection of related objects
- offers methods to add new item to the collection, retrieve item, etc.
To keep track of where Blue has been,
create an instance variable in Blue to hold an ArrayList of Point objects.
- Override the addedToWorld method to add the Blue's initial position to the list when added to the world.
- When an arrow key (right, left, up, or down) is pressed, Blue moves 5 cells in the corresponding direction and the new position is added to the ArrayList.
- When Blue moves, they leave a love trace (a sprite of your choice).
- You will need to make a class to represent the trail.
- If Blue sits in the same place without moving, do not keep adding points to the ArrayList.
- You should check to see if Blue's current location is the same as the last item in the ArrayList.
- If so, don't add the position.
Creating Pinky Pink
When it has been 100 frames since Pink was at the same position as Blue,
Pink starts following the route Blue took by repeating the following steps:
- if Pink does not have a target, then remove the first item from the list of positions and make that the target.
- If there is a target now, turn towards the target and move forward by speed. You can set rotation back to 0 again afterwards.
- When Pink has found Blue, a heart should appear on Blue and pink resets the counter of time since Pink has caught blue.
ArrayList Reference and Examples
Importing the ArrayList:
import java.util.ArrayList;
Creating an empty ArrayList:
ArrayList<Actor> actors = new ArrayList<Actor>(); // stores a list of actors
ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList<Point>(); // stores a list of points
More ArrayList methods:
| method name |
return type |
description |
| boolean |
add(E element) |
Appends the specified element to the end of this list |
| E |
get(int index) |
Returns the element at the specified index in this list |
| E |
remove(int index) |
Remove and returns the element at the specified index |
| int |
size() |
Returns the number of elements in this list |
Note: "E" is the class name of the object the ArrayList contains.
If an ArrayList contains many points, "E" means "Point".
To learn more about ArrayList, you can
read Java's official documentation here,
or read CHS AP Computer Science's lesson on ArrayList
Point Reference and Examples
Importing the Point:
Creating a new Point:
Point newPoint = new Point(100, 200); // x is 100, y is 200
More Point methods:
| method name |
return type |
description |
| distance(double px, double py) |
double |
Returns the distance from this Point to another x y coordinate |
| distance(Point2D pt) |
double |
Returns the distance from this Point to a another Point |
| static distance(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) |
double |
Returns the distance between two points whose coordinates are provided in the parameter |
To learn more about Point, you can
read Java's official documentation here.
You must Sign In to submit to this assignment


